2020 W Rochelle Rd Irving, TX 75062
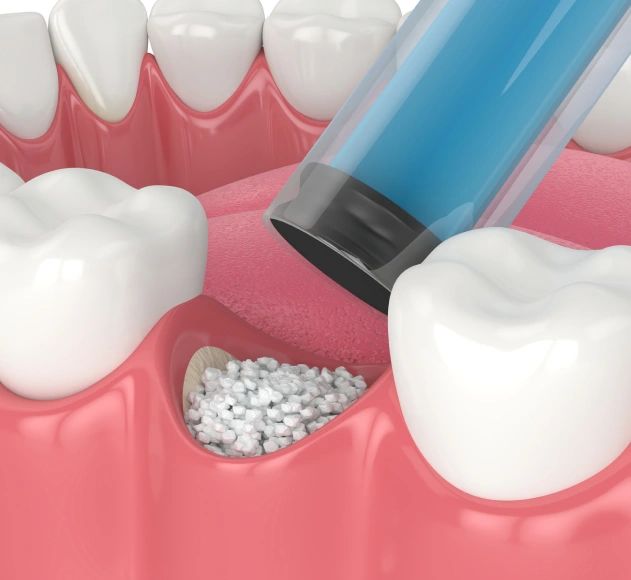
Rebuilding Lost Bone With Modern Dental Techniques
Are you feeling anxious about the thought of bone grafting and augmentation? It's understandable. These procedures may sound intimidating, but they are actually quite common in dentistry. They can help restore your smile and improve your oral health significantly.
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that involves taking bone from one area of the body and placing it in another area. The bone can come from the patient, or it can be donated bone. Bone grafting is often used to repair bones that are not healing properly, or to build up an area of the bone that has been lost due to injury or disease.
A Few Facts of Bone Grafting and Augmentation
Did you know that over 500,000 people in the United States have bone grafting and augmentation procedures each year? This number is expected to grow as more people learn about the benefits of these procedures. Bone grafting and augmentation can be used to improve the overall health of your teeth and jawbone.
These procedures can also be used to improve the appearance of your smile by increasing the size and strength of your teeth. The American Academy of Implant Dentistry (AAID) is a leading authority on these procedures. Here are a few facts about bone grafting and augmentation from the AAID:
- Bone grafting is a procedure that involves using donor bone to replace missing or damaged bone in your jawbone.
- Augmentation is a procedure that uses donor tissue to add volume to your existing jawbone.
- Both procedures can be performed at the same time or separately.
- The success rate for both procedures is very high, with most patients seeing significant improvements in their oral health.
Why is Bone Grafting Necessary?
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that replaces missing bone to repair bones or joints that have been damaged by injury or disease. The graft may be taken from another area of the patient's body, or it may be a synthetic substitute. Bone grafting is often necessary to provide structural support for dental implants. It can also improve the function and appearance of damaged bones or joints.
If you're considering bone grafting and augmentation to improve the look of your smile, it's important to choose a qualified dentist who has experience with this type of procedure. Here are some questions to ask when selecting a bone grafting and augmentation dentist:
- What is your experience with performing bone grafting and augmentation procedures?
- How long will the results last?
- Are there any risks or complications associated with this procedure?
- What is the recovery time like after this procedure?
- How much does this procedure cost?
- Do you offer financing options for this procedure?
- Will my insurance cover this procedure?
- When can I schedule an appointment for this procedure?
What Kinds of Bone Grafting Procedures Are There?
There are four primary types of bone grafting procedures: autogenous, allograft, xenograft, and alloplastic.
Autogenous bone grafting is the process of taking bone from one area of the body and using it to repair or replace damaged bone in another area of the body. This type of graft is often considered the gold standard because it uses the patient’s tissue, which reduces the risk of rejection or infection.
Allograft bone grafting involves using bone from a donor. Allografts are carefully screened to minimize the risk of disease transmission. They can be used for small or large defects and are often used in conjunction with other types of grafts.
Xenograft bone grafting uses the animal bone to repair human bones. The most common source of animal bone is cows. Xenografts are processed to remove all cells and proteins that could cause an immune reaction in humans. Like allografts, they can be used for small or large defects.
Alloplastic bone grafting uses man-made materials to replace or support damaged bones. The two most common materials used in this type of graft are hydroxyapatite (HA) and tricalcium phosphate (TCP). Both HA and TCP are similar to natural human bones and promote new bone growth.
How is Bone Grafting Performed?
There are several ways that bone grafting can be performed, depending on the specific procedure. The most common type of bone grafting is autogenous, which uses bone taken from another area of the patient's body. Allografts use bone from a donor, while artificial bones can also be used.
The first step in any type of bone grafting is to make an incision in the gums so that the surgeon can access the underlying bone. Next, a small amount of bone is removed from the chosen location and then placed in the area where more bone is needed. In some cases, metal screws or plates may be used to secure the graft in place.
Once the graft has been placed, it will take time for it to fuse with the existing bone. During this healing process, patients will need to follow strict oral hygiene instructions and avoid putting too much pressure on the grafted area. Once healed, the new bone will help support dental implants or other dental prosthetics.
What Are the Risks and Complications Associated With Bone Grafting?
What is the Recovery Time for Bone Grafting?
Recovery time for bone grafting can vary depending on the type of graft performed. For example, autogenous (using your tissue) or allogeneic (using donor tissue) grafts typically have a longer recovery time than an artificial bone graft. Additionally, the size and location of the grafted area can affect recovery time.
Most people report feeling back to normal within two to four weeks after bone grafting surgery. However, it is important to follow your surgeon's instructions for postoperative care, which may include taking it easy and avoiding severe activity for several weeks after surgery. This will help ensure that your body has adequate time to heal and reduce the risk of complications.


